Interactive Mapmaking with Python
Sangarshanan
Data + Pandas <3¶

import pandas
df = pandas.read_csv('data/cities.csv')
df.head()
| name | longitude | latitude | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Vatican City | 12.453387 | 41.903282 |
| 1 | San Marino | 12.441770 | 43.936096 |
| 2 | Vaduz | 9.516669 | 47.133724 |
| 3 | Luxembourg | 6.130003 | 49.611660 |
| 4 | Palikir | 158.149974 | 6.916644 |
Data with a location component¶
Geometries
- Point (latitude, longitude)
- Polygon [point1, point2]
We can also have linestrings, multipolygons, circles etc
Enter GeoPandas¶
- Work with a Familiar interface (Dataframes), in this case Geodataframes
- Read/ write GIS data (Fiona) formats like shapefile, geojson, kml etc
- Perform spatial operations like merge/join/overlay etc (Shapely)
- Plot em on a map (Matplotlib)
Also a whole lot of other things like handling projections, recently added vectorized geometrical operations, Indexing with rtree... and more such goodies
Interested in more, https://github.com/jorisvandenbossche/geopandas-tutorial has a comprehensive tutorial by the maintainer
df.head()
| name | longitude | latitude | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Vatican City | 12.453387 | 41.903282 |
| 1 | San Marino | 12.441770 | 43.936096 |
| 2 | Vaduz | 9.516669 | 47.133724 |
| 3 | Luxembourg | 6.130003 | 49.611660 |
| 4 | Palikir | 158.149974 | 6.916644 |
import geopandas
# Converting latitude, longitude to geometry object
gdf = geopandas.GeoDataFrame(
df, geometry=geopandas.points_from_xy(df.longitude, df.latitude))
# setting the projection
gdf.crs = 'epsg:4326'
gdf.head()
| name | longitude | latitude | geometry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Vatican City | 12.453387 | 41.903282 | POINT (12.45339 41.90328) |
| 1 | San Marino | 12.441770 | 43.936096 | POINT (12.44177 43.93610) |
| 2 | Vaduz | 9.516669 | 47.133724 | POINT (9.51667 47.13372) |
| 3 | Luxembourg | 6.130003 | 49.611660 | POINT (6.13000 49.61166) |
| 4 | Palikir | 158.149974 | 6.916644 | POINT (158.14997 6.91664) |
How do I plot em ?¶
With geopandas, its as simple as .plot()¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
gdf.plot()
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x7f07cabfb710>

Folium Plots¶
gdf.head(1)
| name | longitude | latitude | geometry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Vatican City | 12.453387 | 41.903282 | POINT (12.45339 41.90328) |
# import the library
import folium
# Create a map with a center and zoom level
mapa = folium.Map(location= [-15.783333, -47.866667],
zoom_start= 1,
tiles= "OpenStreetMap")
mapa
# Add the geodataframe as a geojson feature
points = folium.features.GeoJson(gdf,
# tooltip with the name
tooltip=folium.GeoJsonTooltip(fields=['name']))
# Adding the feature to the canvas we created
mapa.add_child(points)
mapa
Onward to Polygons¶
world = geopandas.read_file(geopandas.datasets.get_path('naturalearth_lowres'))
world.head(2)
| pop_est | continent | name | iso_a3 | gdp_md_est | geometry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 920938 | Oceania | Fiji | FJI | 8374.0 | MULTIPOLYGON (((180.00000 -16.06713, 180.00000... |
| 1 | 53950935 | Africa | Tanzania | TZA | 150600.0 | POLYGON ((33.90371 -0.95000, 34.07262 -1.05982... |
#https://matplotlib.org/3.1.1/gallery/color/colormap_reference.html
world.plot(figsize=(20,5), column= 'gdp_md_est', cmap='YlGnBu', legend=True)
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x7f07d3faecc0>
import branca.colormap as cm
colormap = cm.linear.YlGnBu_09.to_step(data=world['gdp_md_est'], n=9)
colormap
m = folium.Map()
# Setting the style
style_function = lambda x: {
# How to fill color of the polygon
'fillColor': colormap(x['properties']['gdp_md_est']),
# Color of Polygon
'color': 'black',
# Weight of the border (Around the Polygon)
'weight': 0.5,
# Opacity of filled color
'fillOpacity': 0.75
}
# Creating a geojson map with the style
folium.GeoJson(
world,
tooltip=folium.GeoJsonTooltip(fields= ["name", "gdp_md_est"]),
style_function=style_function
).add_to(m)
# Add the legend to the same canvas
colormap.add_to(m)
m
Marker Clusters¶
from folium.plugins import MarkerCluster
locations = []
# City location geometries to a list of latlongs pairs
for idx, row in gdf.iterrows():
locations.append([row['geometry'].y, row['geometry'].x])
# Empty canvas
m = folium.Map()
# Markercluster
m.add_child(MarkerCluster(locations=locations))
m
Heatmap¶
from folium.plugins import HeatMap
m = folium.Map()
m.add_child(HeatMap(locations, radius=15))
m
Mo data Mo Problems

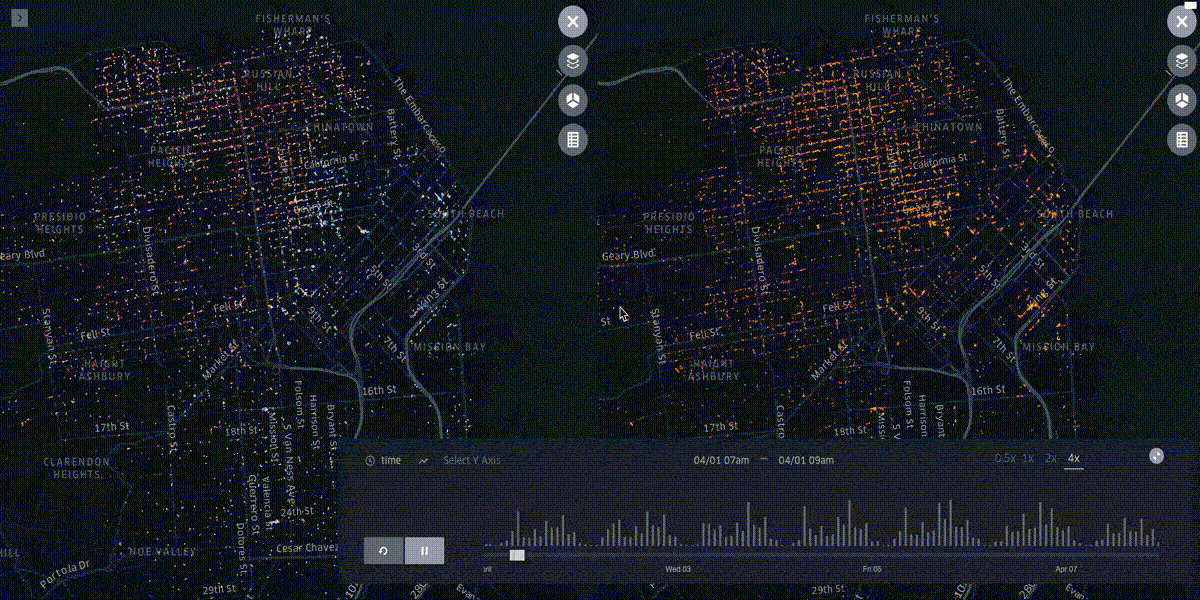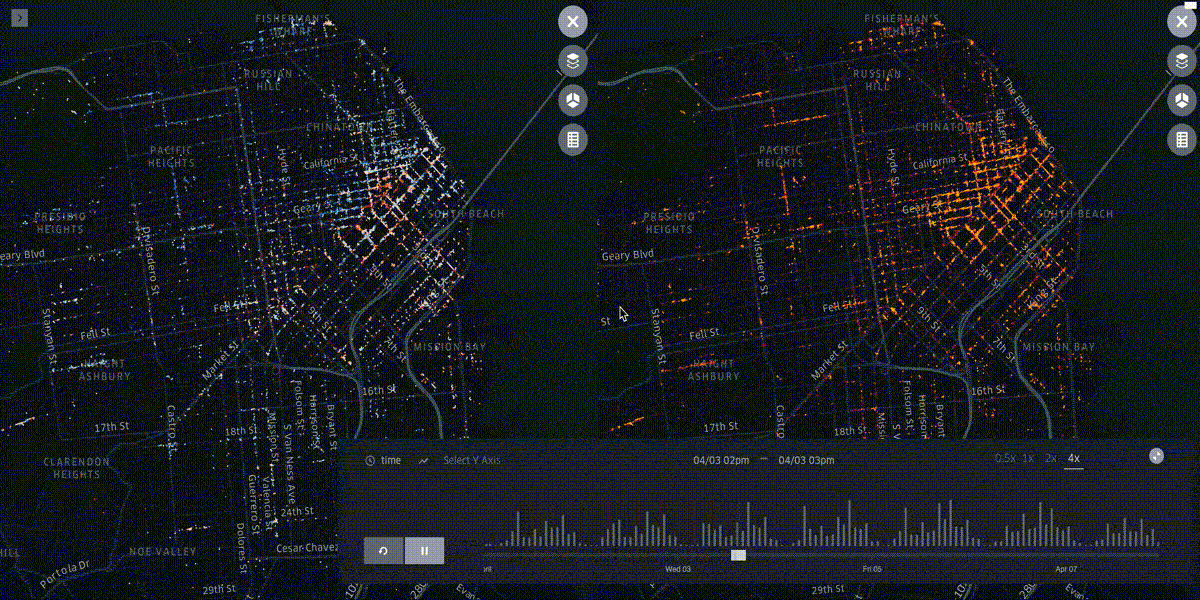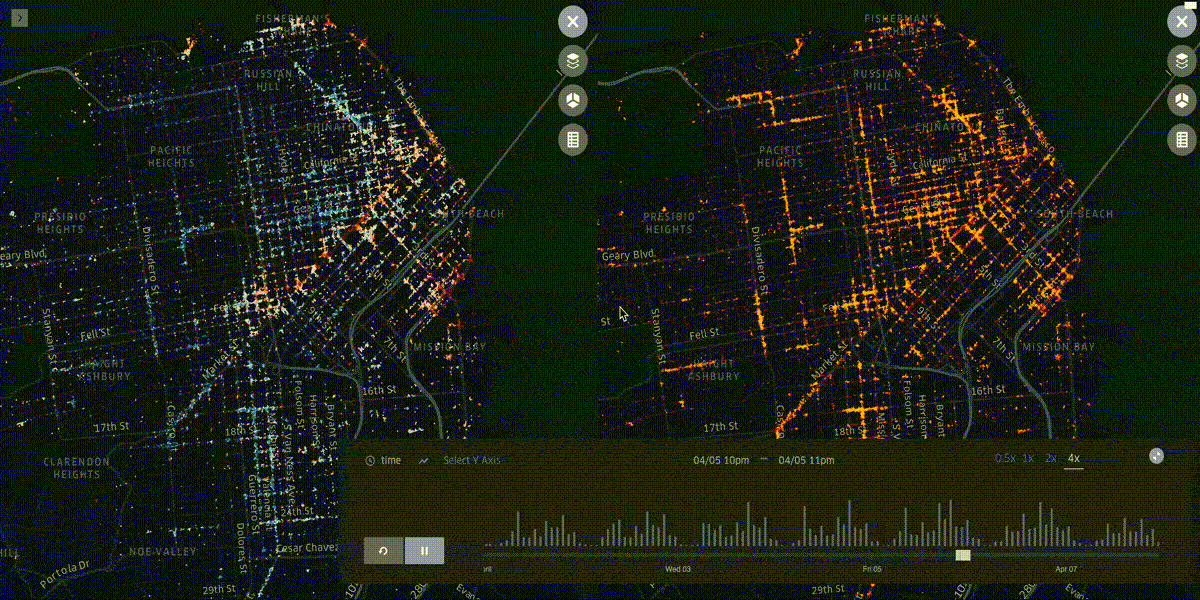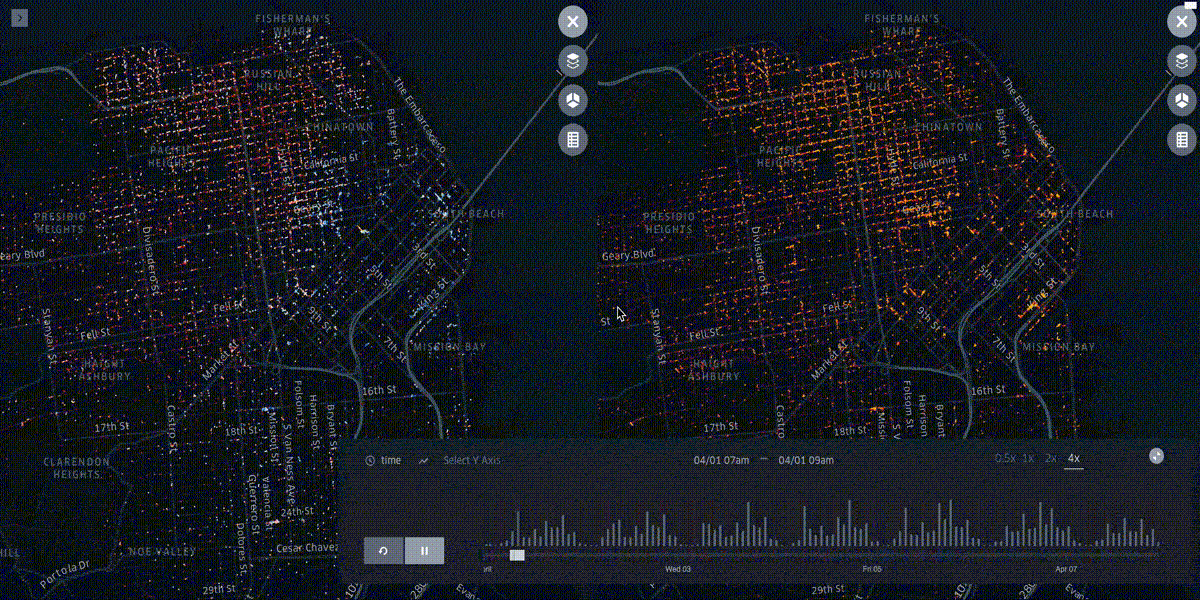
kepler.gl¶
Kepler.gl is a data-agnostic, high-performance web-based application for visual exploration of large-scale geolocation data sets. Built on top of Mapbox GL and deck.gl, kepler.gl can render millions of points representing thousands of trips and perform spatial aggregations on the fly.
Jupyter Notebook > 5.3
pip install keplergl
JupyterLab
jupyter labextension install @jupyter-widgets/jupyterlab-manager keplergl-jupyter

Kepler uses config to customize its maps¶
{
"version": "v1",
"config": {
"visState": {
"filters": [
{
"dataId": "earthquakes",
"id": "vo18yorx",
}
],
"layers": [
{
"id": "hty62yd",
"type": "point",
"config": {
"dataId": "earthquakes",
"label": "Point",
"color": [
23,
184,
190
],
"columns": {
"lat": "Latitude",
"lng": "Longitude",
"altitude": null
},
.....
The UX flow is composed of five layers¶
Filters, Timelines and other cool perks¶


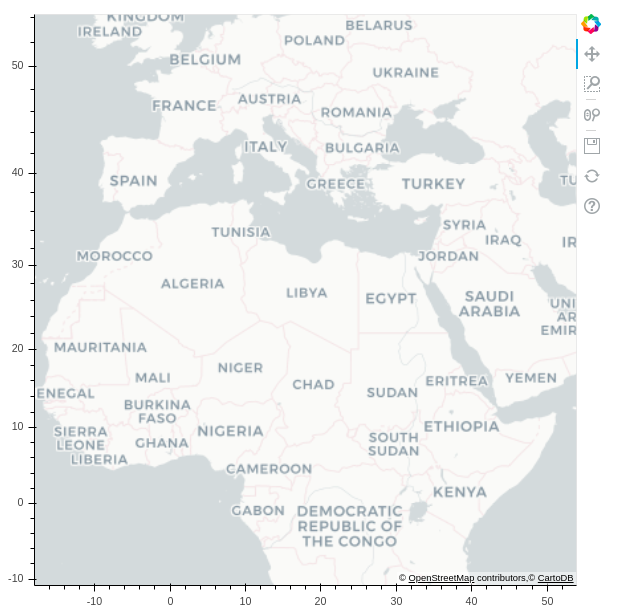
Bokeh¶
from bokeh.io import output_notebook
from bokeh.plotting import figure, output_file, show
from bokeh.tile_providers import CARTODBPOSITRON, get_provider
output_notebook()
tile_provider = get_provider(CARTODBPOSITRON)
p = figure(x_range=(-2000000, 6000000), y_range=(-1000000, 7000000),
x_axis_type="mercator", y_axis_type="mercator")
p.add_tile(tile_provider)
show(p)
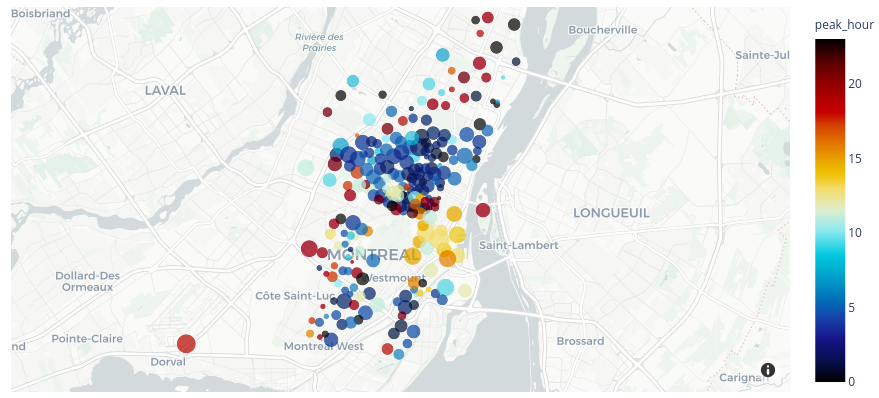
Plotly¶
import plotly.express as px
df = px.data.carshare()
fig = px.scatter_mapbox(df, lat="centroid_lat", lon="centroid_lon", color="peak_hour", size="car_hours",
color_continuous_scale=px.colors.cyclical.IceFire, size_max=15, zoom=10,
mapbox_style="carto-positron")
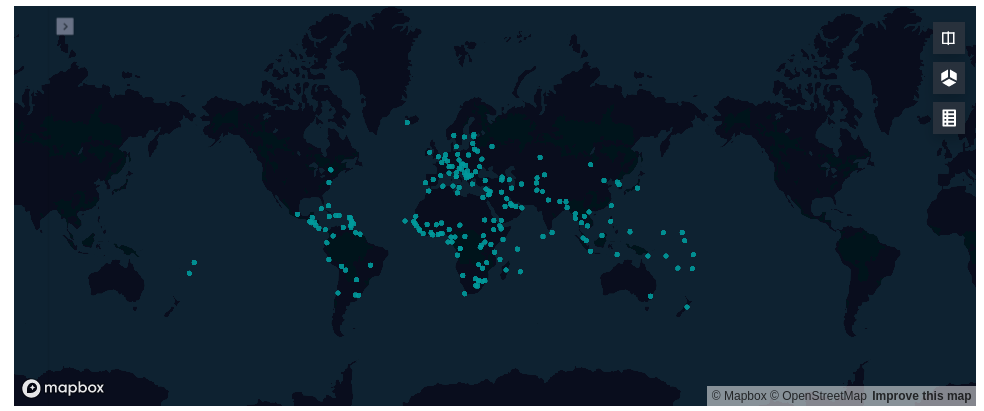
Say hello to Geopatra 👋¶
import geopatra
gdf.folium.plot(zoom=2)
Yet another one, why ?¶
- Different libraries have different APIs
- All of them are awesome and have something new and exciting and offer
- Netflix Syndrome
- I wanna be able to switch between them without having to remember all the interfaces/ spend time googling
Chloropeth maps¶
world.folium.chloropeth(color_by= 'pop_est',
color= 'green',
zoom= 1,
style = {'color': 'black',
'weight': 1,
'dashArray': '10, 5',
'fillOpacity': 0.5,
})
Circle Plots¶
gdf.folium.circle(radius=10, fill=True, fill_color='red', zoom=100, color='blue')
Markercluster¶
gdf.folium.markercluster(zoom=1, tooltip=["name"])
Weighted Markercluster¶
import random
gdf['value'] = [int(random.randint(10, 1000)) for i in range(len(gdf))]
gdf.folium.markercluster(zoom=1, metric='sum', weight='value')
Heatmap¶
gdf.folium.heatmap(style={'min_opacity': 0.3}, zoom=5)
Kepler.gl¶
from IPython.display import IFrame
kmap1 = gdf.kepler.plot()
User Guide: https://docs.kepler.gl/docs/keplergl-jupyter

Thank You : )
